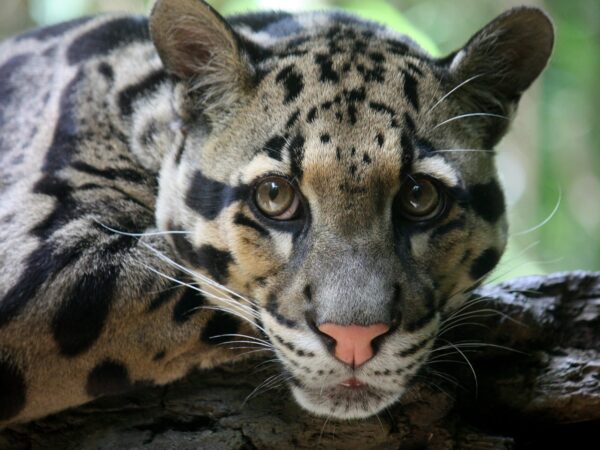
Beyond border: securing big cats and their habitats across the Chittagong–Lushai transboundary landscape of Bangladesh and India
Project description
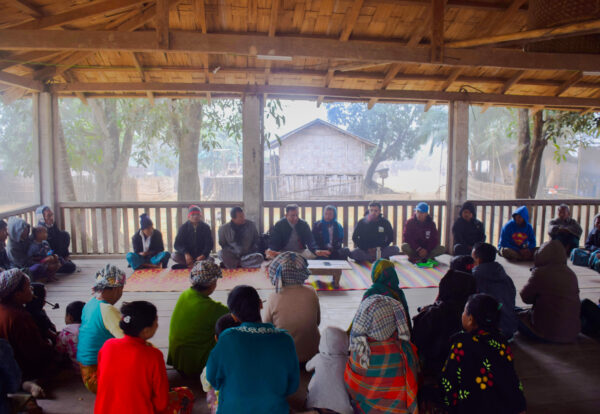
The Chittagong-Lushai Big Cat Conservation Project aims to ensure the long-term survival of endangered big cats and restore the ecological health of their transboundary habitat across Bangladesh and India. This pioneering initiative integrates robust scientific monitoring with community-led conservation, sustainable livelihood development, and cross-border policy collaboration. By empowering local communities, especially women and youth, as primary stewards of their natural resources, the project seeks to create a resilient, shared landscape where both wildlife and people can thrive. It serves as a replicable model for effective, inclusive transboundary conservation in South and Southeast Asia.
This project is implemented by Arannayk Foundation.
Threats

Habitat loss & degradation
Human-wildlife conflict

Over-exploitation of natural resources & prey depletion
Project objectives
- Generate and apply scientific knowledge to guide conservation through advanced ecological monitoring and research;
- Improve habitats, restore ecological connectivity, and promote sustainable, climate-resilient livelihoods to support big cats and their prey;
- Enhance awareness and empower local communities, particularly women and youth, to actively participate in conservation; and
- Evaluate conservation impacts on species, prey, habitats, and biological corridors through long-term monitoring of biological and socio-economic indicators.
Project activities
- Establish a robust platform for transboundary governance, policy coordination, and information sharing between Bangladesh and India.
- Conduct targeted ecological monitoring and baseline assessments to accurately map big cat populations, prey availability, and movement corridors.
- Significantly enhance anti-poaching and forest protection efforts through the capacity building of local enforcement and community patrol teams.
- Implement large-scale habitat restoration and enrichment activities across fragmented forest areas to improve ecological connectivity and refuge.
- Promote sustainable and forest-friendly alternative livelihoods to decrease pressure from local communities on natural resources and the forest ecosystem.
- Develop and execute comprehensive strategies for mitigating human-wildlife conflict and improving community safety in interface areas.







